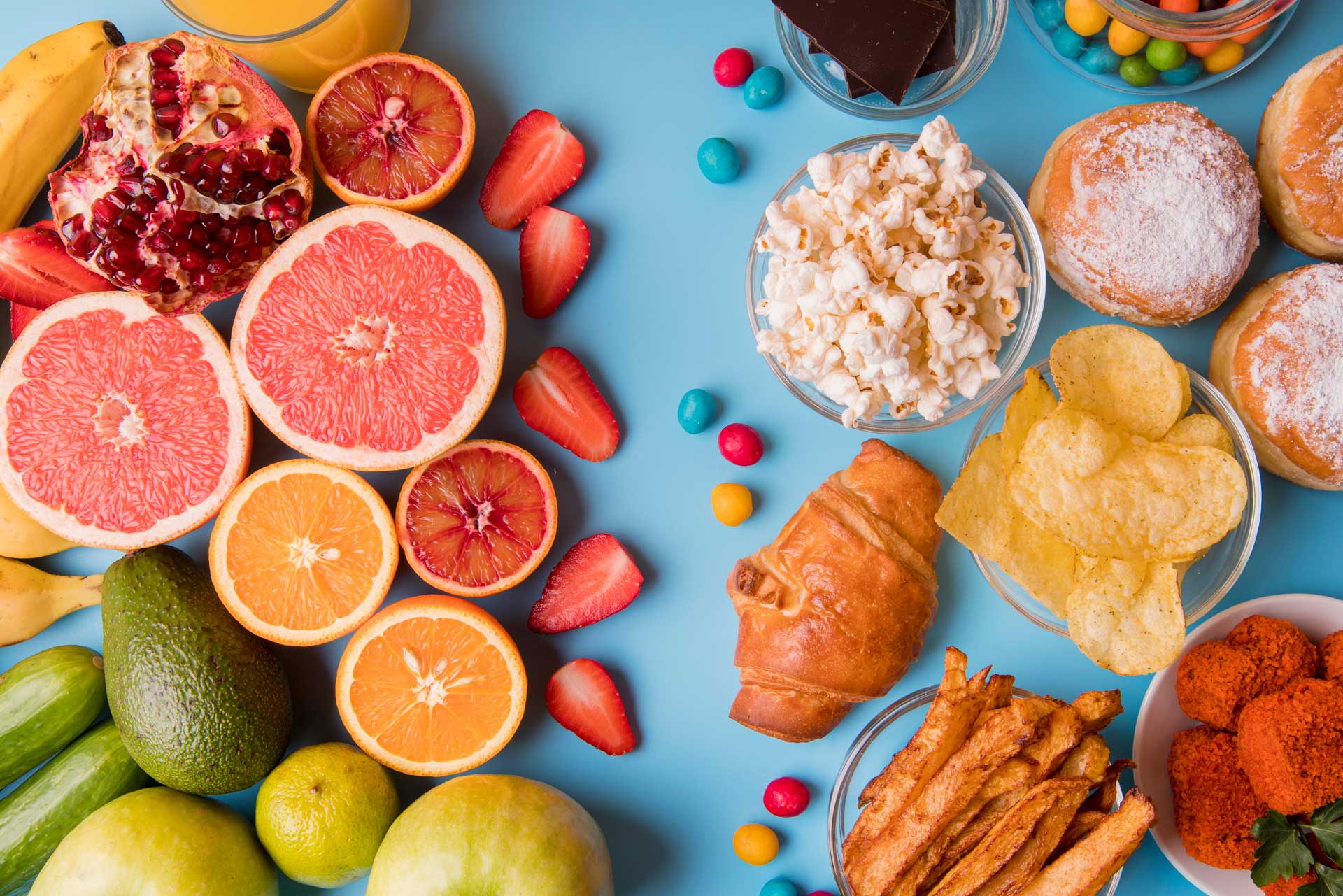
The causes of obesity include sociodemographic, behavioral (nutrition and lifestyle), and genetic factors.Sociodemographic factors can be listed as advanced age, being married, low-income level, being a woman, migration from village to city, and easy accessibility to junk food and packaged foods.
Behavioral factors include eating habits and lifestyle. Nutritional habits are an important determining factor not only for obesity, but also for our health. Confectionery, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, candies, pastries, processed food consumption, monotonous diet, and consuming foods high in saturated fat may increase the risk of obesity. Increased inactivity by staying in front of a screen for a long time, short sleep periods, shift work systems, stress, smoking, and constant use of vehicles for transportation are among the causes of obesity. Stress can increase your appetite through hormonal means, resulting in the production of belly fat.
Genetic factors include family history of obesity and obesity-related genes. As a result of research conducted by Harvard Health School, it has been found that genes contribute less to the development of obesity than environmental factors.
- The rate of obese individuals (BKI ≥30 kg/m2) aged 15 and over was 21.1% in 2019 and 20.2% in 2022.
- When looked at on a gender basis, it was found that 23.6% of women were obese and 30.9% were overweight in 2022;16.8% of men were obese and 40.4% were overweight.
- A study in 300 healthy volunteers found that BMI was reduced in those who frequently consumed gojiberries, cranberries, and pomegranates, as opposed to those who never consumed these functional foods.
- The results of a meta-analysis showed that individuals consuming green tea catechins along with caffeine had reduced BMI, body weight, and waist circumference.
- A meta-analysis published in 2018 found that administration of probiotics led to a significant reduction in body weight, BMI, and fat percentage compared to placebo.
- It is known that capsaicin, the bioactive component of hot pepper, stimulates thermogenesis and reduces hunger. Some studies have found that hot pepper consumption is related to decreasing BMI, body fat, waist-hip ratio and increasing muscle mass.
- Fruits are rich in polyphenols such as anthocyanidins, fiber and vitamins. Consumption of fruit, and especially pomegranate, is associated with reduced BMI. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) stated that the intake of cranberries and cranberry products has benefits such as reducing anthropometric measurements such as body weight, BMI, waist circumference, and helping to maintain a normal weight.
- Although nuts are rich in fatty compounds, they may be associated with maintaining body weight, aiding weight control, and increasing satiety.
- Moderate consumption of olive oil and avocado has been observed to reduce BMI.
Al-Raddadi R et al. The prevalence of obesity and overweight, associated demographic and lifestyle factors, and health status in the adult population of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The Adv Chronic Dis (2019).
Borgeraas H et al. Effects of probiotics on body weight, body mass index, fat mass and fat percentage in subjects with overweight or obesity: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev (2018).
Endalifer ML and Diress G. Epidemiology, predisposing factors, biomarkers, and prevention mechanism of obesity: A systematic review. J Obes (2020).
Konstantinidi M and Koutelidakis AE. Functional foods and bioactive compounds: A review of its possible role on weight management and obesity’s metabolic consequences. Medicines (2019).
Liu BN et al. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J Gastroenterol (2021).
Narciso J et al. Behavioral, contextual and biological factors associated with obesity during adolescence: A systematic review. PloS one (2019).
Nataraj BH et al. Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb Cell Factories, (2020).
Nina Zorfass. What Is Functional Nutrition? (2022).
Ntrigiou V et al. Functional food consumption correlates with anthropometric characteristics and body composition in healthy adults. Curr Topics Nutraceut Res (2018).
Phung OJ et al. Effect of green tea catechins with or without caffeine on anthropometric measures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr (2010).
Shaikh S. Sources and health benefits of functional food components. Curr Topics Funct Food (2022).
Türkiye Beslenme Rehberi TÜBER 2022, T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı Yayın No: 1031, Ankara 2022.
Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu (TÜİK), Türkiye Sağlık Araştırması 2022 (01 Haziran 2023).
WHO, Obesity and overweight (2021).
Wollner M et al. Accuracy of the WHO's body mass index cut-off points to measure gender-and age-specific obesity in middle-aged adults living in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Public Health Res (2017).
Zohoori FV. Nutrition and Diet. The Impact of Nutrition and Diet on Oral Health (2020).