- Diabetes and insulin resistance
- Obesity and unhealthy eating,
- Smoking and use of other tobacco products,
- Hypercholesterolemia (high LDL cholesterol),
- Hypertension (high blood pressure),
- Inflammatory diseases (psoriasis, arthritis, etc.)
- Sleep apnea
- Sedentary and stressful life
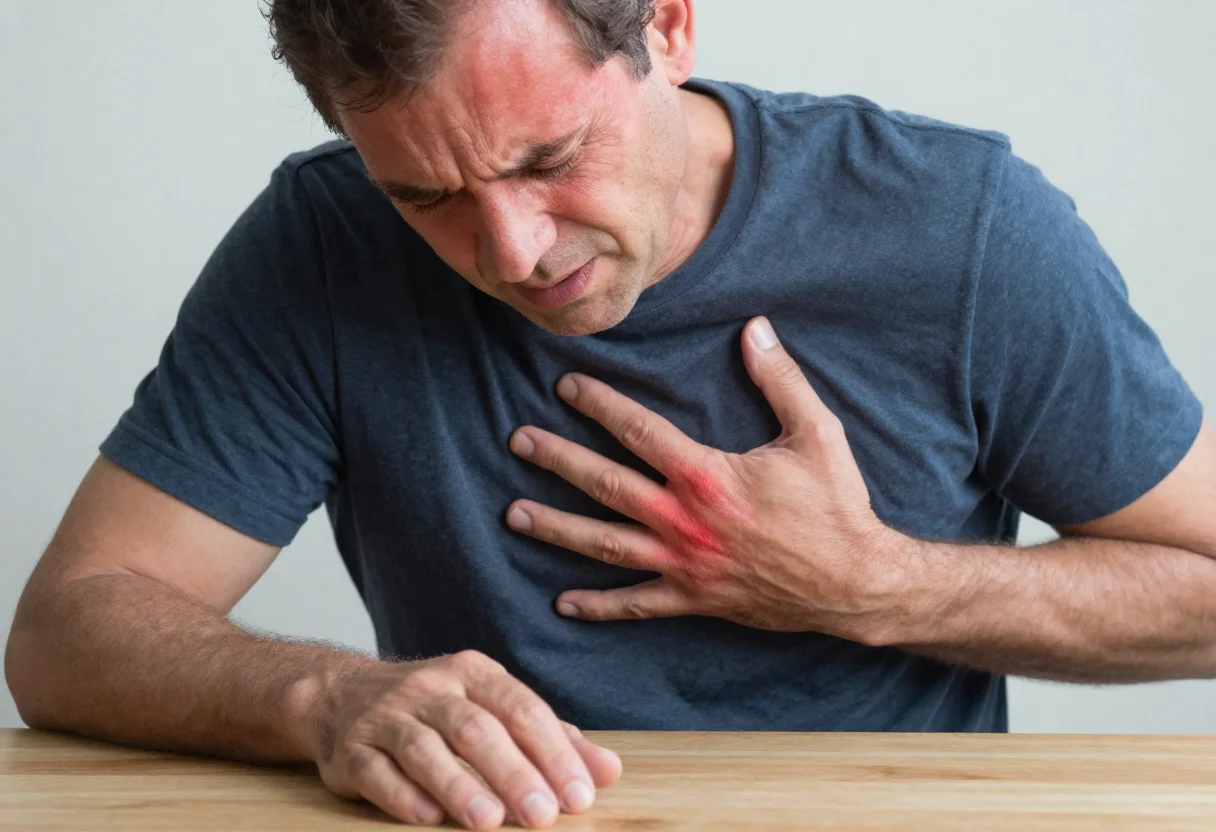
- Chest pain (with or without exertion)
- Numbness or weakness in the arms and legs
- Severe headache
- Speech difficulties
- Stroke (Cerebrovascular Event (CVE))
- Visual disturbances
- Advanced age
- Diabetes
- Hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol)
- Sedentary life
Pain is the most important symptom in atherosclerotic blockages, and tests and treatment are performed according to the blocked organ. For atherosclerosis, a physical examination should be performed and the history of the disease should be listened to. Ultrasound, ECG (electrocardiography), ECHO (echocardiography), stress test and cardiac scintigraphy are among the diagnostic methods. Angiography is recommended for the definitive diagnosis of atherosclerosis. ECG is the process of recording electrical activity in the heart to study the functioning of the heart muscle and the neurotransmission system. It is very important that the ECG also shows something suggestive of acute ischemia (ST wave elevation on the ECG). ECGs suggestive of an acute ischemic condition are cardiac emergencies. They include situations where the patient needs urgent angiography. Echo is the process of visualizing the walls of the structures of the heart. Detection of any wall motion defects in the walls of the heart may be the result of a previous heart attack due to possible atherosclerosis. The effort test is performed by walking the patient on a treadmill and the patient's ECG is taken during the effort and examined for any ECG changes. Patients with a positive effort test are scheduled for angiography under elective conditions. Angiography: A dye called contrast is injected into the coronary artery with the help of thin and soft catheters and the inside of the vessel is visualized with X-rays. Angiography can be performed for many vessels.
In the treatment of atherosclerosis, it is recommended to stop using tobacco products and to establish a healthy diet. In patients with high cholesterol, it is important to eat a balanced and regular diet (avoiding the consumption of high carbohydrate and saturated fat foods, etc.), to exercise and to end sedentary life. If deemed necessary by the physician, drug treatment can be initiated with drugs used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), such as statins (such as atorvastatin, rosuvastatin), ezetimibe, and drugs such as low-dose aspirin etc. which prevent the clumping of blood cells called platelets (blood thinners). Today, thanks to advances in technology and medicine, blocked vessels can be opened without surgery with the angiography method. With angioplasty, a non-surgical method, the procedure is performed in 20-30 minutes. With the help of a catheter, the heart vessels are accessed and the diseased vessels are opened with imaging techniques. Bypass (coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)) surgery, which is a surgical method, is one of the applications with a high success rate with comfortable and longer life expectancy.