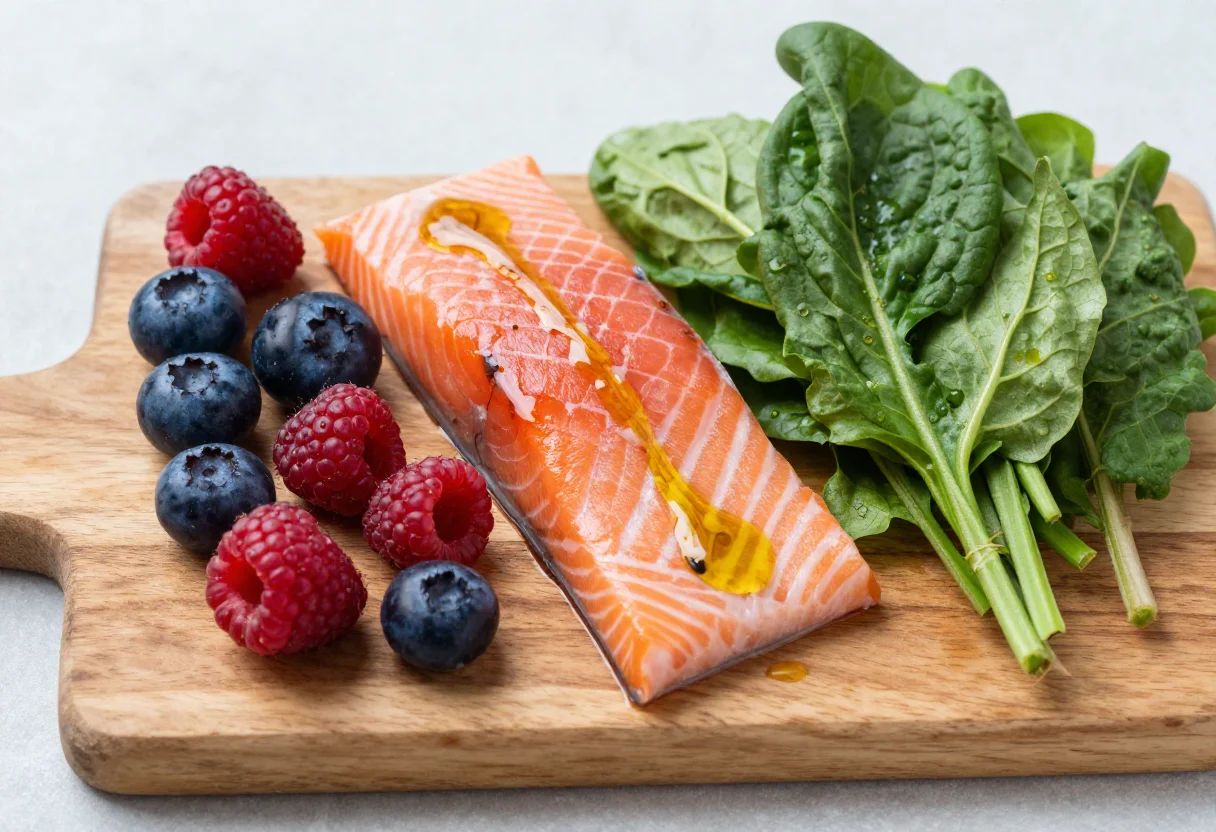
Food sources generally meet the daily calcium needs. The following foods are typically recognized as important calcium sources:
Dairy products: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and kefir are rich in calcium.
Dark green vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, and kale are high in calcium.
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, sesame seeds, and chia seeds are significant sources.
Seafood: Small-boned fish like sardines and anchovies are also good sources of calcium.
Calcium deficiency can be treated with calcium supplements. These are recommended for individuals who do not receive sufficient calcium from food.
For the body to effectively use calcium, it must first be absorbed through the intestines. Factors affecting this process include:
Vitamin D: Proven to enhance calcium absorption and aid its transfer to bone tissue.
Phosphorus and Magnesium: When balanced, they support bone health; however, excessive phosphorus intake may reduce calcium's effectiveness.
Food content: Compounds such as oxalates and phytates (found in whole grains and some vegetables) have been shown to inhibit calcium absorption.
Stomach acid level: Low stomach acid can reduce calcium absorption.
Calcium levels are typically assessed using a blood test, and the expected range is as follows:
- Total Calcium (Serum Calcium): 8.5 - 10.5 mg/dL
- Ionized Calcium: 4.5 - 5.6 mg/dL. These values may vary slightly depending on the testing laboratory. Levels below or above these ranges may indicate various health complications. Low levels cause hypocalcemia, and high levels cause hypercalcemia.
Hypocalcemia (Calcium Deficiency): This imbalance can manifest with symptoms such as muscle spasms, bone loss, tooth decay, and disruptions in nerve transmission.
Hypercalcemia (Calcium Excess): Elevated calcium levels may lead to health issues like kidney stones, constipation, and heart rhythm disturbances (cardiac arrhythmias).
1. Only milk and dairy products are a source of calcium.
- This is not true; calcium is found in many foods other than dairy products, such as green leafy vegetables, nuts and fish.
2. Calcium is only needed for bones.
- Although calcium is important for bones, it also has many other important functions in the body, such as muscle function, nerve transmission and blood clotting.
3. Calcium supplements are always necessary.
- Most people can get enough calcium from their daily diet, so taking supplements should only be done on the advice of a doctor.
4 .Increasing calcium intake is enough to strengthen bones.
- Bone health is not only about calcium; factors such as vitamin D, magnesium and regular exercise are also very important for bone health.
5. Taking calcium supplements prevents osteoporosis.
- Although calcium supplements support bone health, diet, exercise and other lifestyle factors should be considered to prevent osteoporosis.
6.Calcium supplements do not cause kidney stones.
- On the contrary, excessive intake of calcium supplements can lead to kidney stone formation, so it is important not to exceed the recommended amount.
7.Increasing calcium intake increases the risk of high blood pressure.
- Calcium can actually stabilise blood pressure and control high blood pressure. On the contrary, adequate calcium intake can lower blood pressure.
8.Excess calcium is excreted from the body, it does no harm.
- Excess calcium can accumulate in the body and cause kidney stones, constipation and heart problems. Therefore, excessive intake should be avoided.