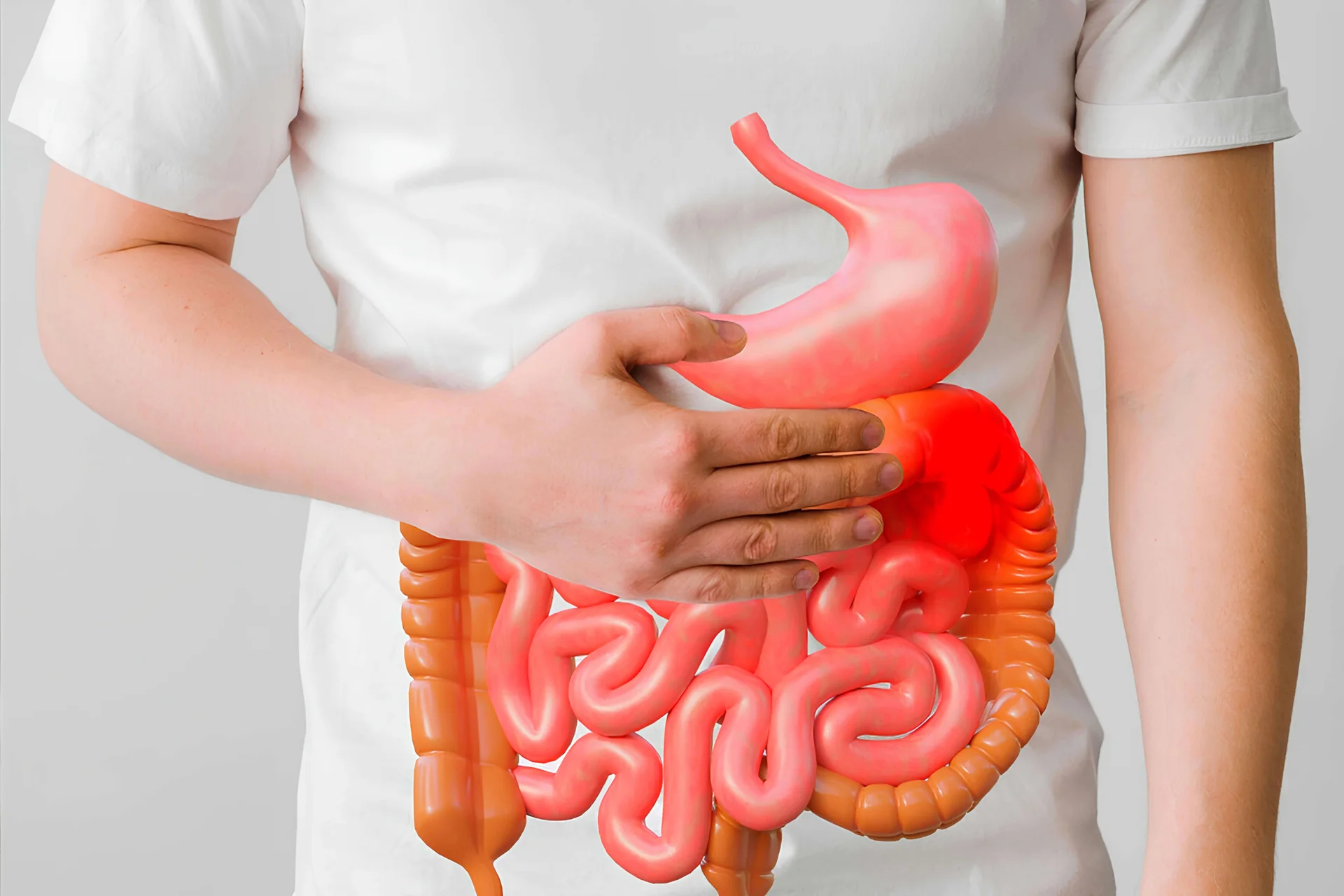
Crohn's disease is an aggressive and slowly progressing disease with high morbidity. Diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, fever, weight loss, and fatigue are the most common symptoms. The course of the disease can vary from mild symptoms to the need for hospitalization and surgery. In children and adolescents, the initial symptoms may be insidious, such as growth retardation, inadequate sex hormone secretion, joint inflammation, weight loss or fever of unknown origin. In Crohn's patients, abdominal pain is common due to involvement of all intestinal layers. Obstruction due to thickening of the intestinal wall and narrowing of the lumen, nausea and vomiting may occur. Bloody and mucousy diarrhea may be observed. Ulceration around the anus due to diarrhea is common.
Although the course of the disease is different in most patients, perforation, fistula (abnormal connection), abscess and small bowel obstruction are the most common complications of Crohn's disease. There is also an increased incidence of cancer in Crohn's patients. In addition to the digestive system, patients may have inflammatory disorders such as inflammation of the joints, erythema nodosum (inflammation of the subcutaneous fatty tissue), inflammation of the eyes, mucosal aphthous ulcers, sclerosing cholangitis (autoimmune disease of the bile ducts) and liver cirrhosis. Kidney disorders such as nephrolithiasis (kidney stones) due to increased oxalate absorption associated with steatorrhea (fatty stools) have been detected in 1/3 of patients. Amyloidosis (accumulation of a protein called amyloid in tissues) and thromboembolic disease (severe reduction in blood flow due to clots), which are indicators of systemic inflammation, are serious complications of Crohn's disease. In addition, malnutrition is common in patients.
Crohn's disease is a common disease with an increasing prevalence worldwide. Numerous genetic and environmental factors are associated with the development of the disease. Furthermore, dysbiosis plays an important role in the development of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. Smoking, antibiotic intake in early childhood and western-style eating habits are important environmental factors in the etiology of the disease. In recent years, significant progress has been made in understanding the role of intestinal inflammation in the pathogenesis of the disease. These developments have contributed to the investigation of new therapeutic approaches, such as fecal microbiota transplantation, which may be preferred over or supplement existing medical and surgical treatment strategies. Medical nutrition therapy is prominent in preventing symptoms such as diarrhea and abdominal pain, which are common in patients, and in maintaining remission. Consumption of quality fiber or omega-3 fatty acid intake has been shown to prevent intestinal inflammation in humans. The use of probiotics and/or prebiotics in medical nutrition therapy has led to conflicting results and more scientific research is needed.
Basoglu, I. A. and Karakoyun, B. Crohn’s disease: etiology, pathogenesis and treatment strategies. (2023).
Begümhan Ömeroğlu Yel (2018). Sıçanlarda deneysel kolit modelinde Gilaburu’nun (Viburnum opulus L.) olası tedavi edici ve koruyucu etkilerinin araştırılması. Marmara Üniversitesi, Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Beslenme ve Diyetetik Anabilim Dalı, Yüksek Lisans Tezi. (Danışman: Doç. Dr. Berna Karakoyun Laçin)
Dolinger M, Torres J, Vermeire S. Crohn's disease. (2024).
Hülya Buzcu (2024). Sıçanlarda asetik asit ile oluşturulan deneysel kolit modelinde phoenixin-14'ün olası tedavi edici etkilerinin araştırılması. Sağlık Bilimleri Üniversitesi, Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Tıbbi Fizyoloji Anabilim Dalı, Doktora Tezi. (Danışman: Prof. Dr. Berna Karakoyun Laçin)