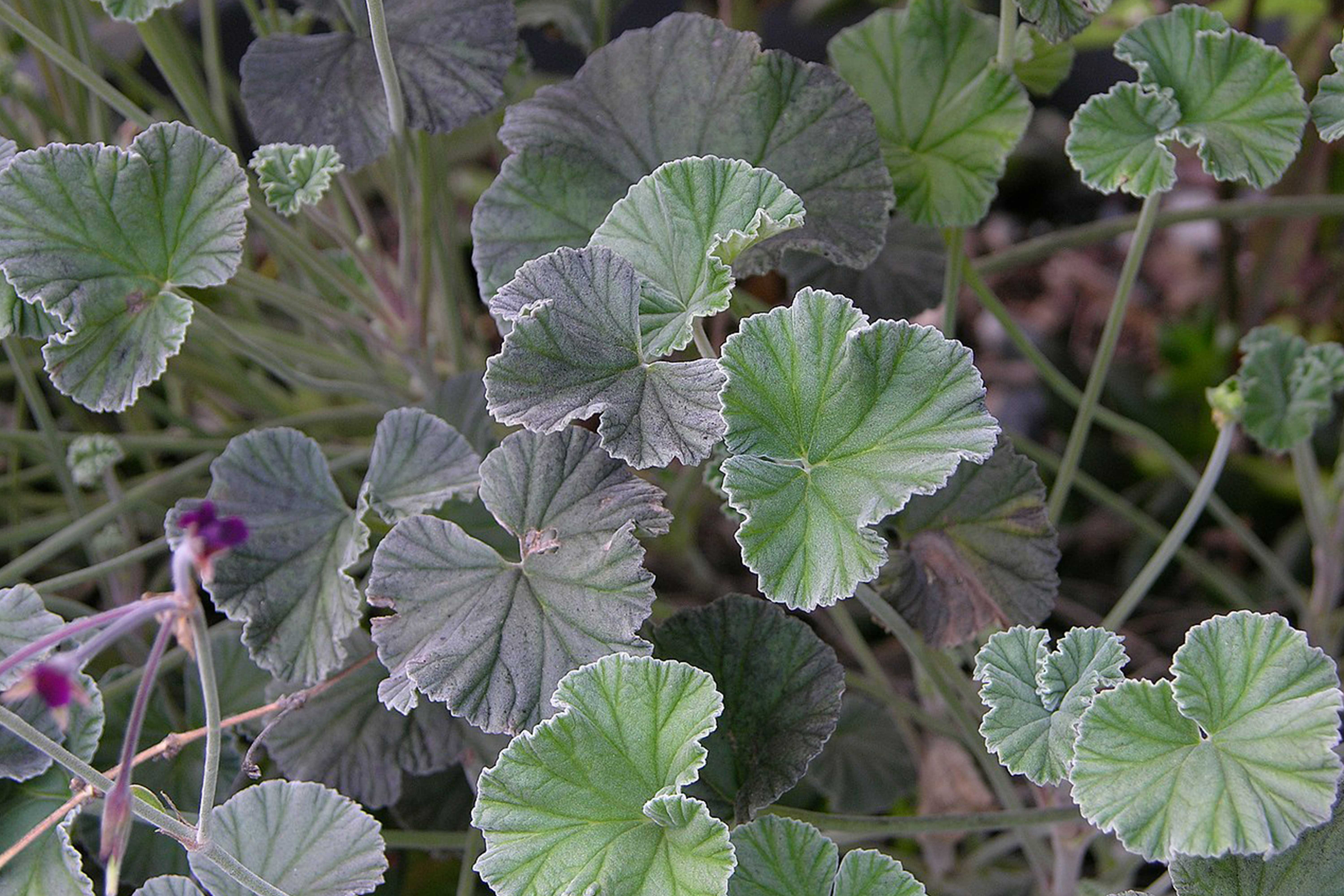
African geranium, botanically known as Pelargonium sidoides, has been cultured in South Africa by indigenous people for many years. It is a medicinal plant utilized as an adjuvant agent supporting the healing process of various diseases.
African geranium has been benefiting for the treatment of folk diseases in traditional and modern medicine. It was known that the root extract of the plant has been pharmaceutically used either solo or inside different dosage forms, tablet, syrup, and oral solutions.
African geranium can be beneficial for the treatment of upper respiratory diseases such as acute bronchitis, tonsillopharyngitis, acute rhinosinusitis, common cold, and other respiratory tract infections in adults. The pediatric usage isn’t limited but concentrated on the symptomatic relief of acute bronchitis; however, it can speed up the healing process of various upper respiratory tract infections as well.
Gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric pain, dysphagia side effects have been commonly observed.
Additionally, type 1 hypersensitivity, bronchospasm, itching, and anaphylaxic shock are rare yet dangerous effects.
- Hypersensitivity
- Mild nose and gum bleeding and gastrointestinal distress (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, etc.)
- Due to lack of sufficient data supporting the safety of its usage by patients on anticoagulant/antiplatelet therapy, it should be avoided.
- It should not be used in patients with liver and kidney disorders.
- It should be discontinued two weeks before surgical operation.
- If the symptoms of the disease do not disappear during the first week of usage or if an undesirable effect is observed, consult a physician.
- It should not be used in children under the age of 6.
- Due to lack of sufficient data supporting the safety of its usage by pregnant and breastfeeding women, it should be avoided.
- The therapy should be supervised by physicians and pharmacists trained especially in herbal products.